Metals such as aluminum and steel require large amounts of energy to produce, and their extraction can result in habitat destruction, pollution, and other environmental harms. In contrast, sustainable materials like bamboo, hemp, or recycled metals can be sourced with a lower environmental footprint. They often require less energy to process and are abundant or renewable resources.
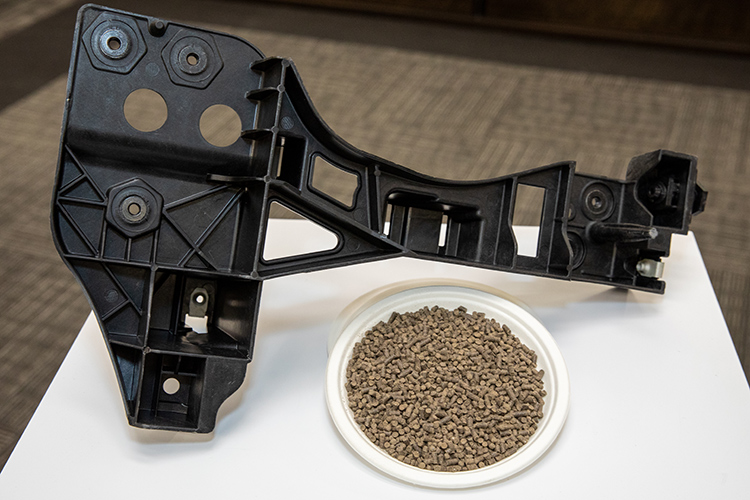
One innovative project is looking at using household waste-based carbon negative materials as an additive in plastic. Even a 5% use of this material can lower carbon footprint by 30%. There has also been a strong advancement with a project that could see hemp-based automotive products such as roof racks in production.
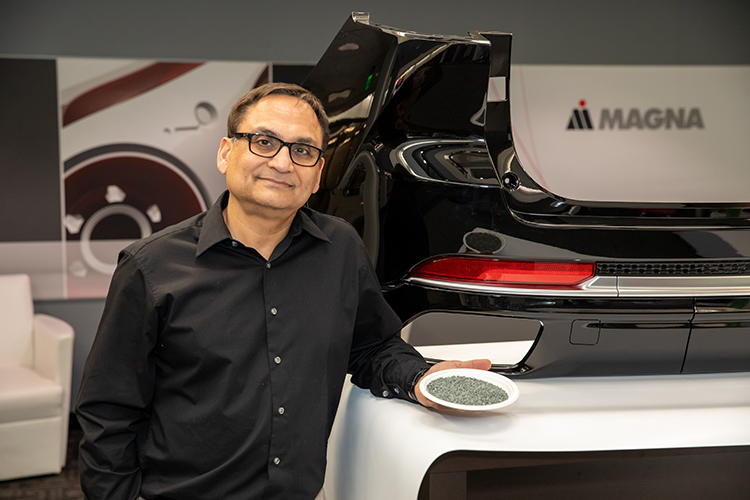
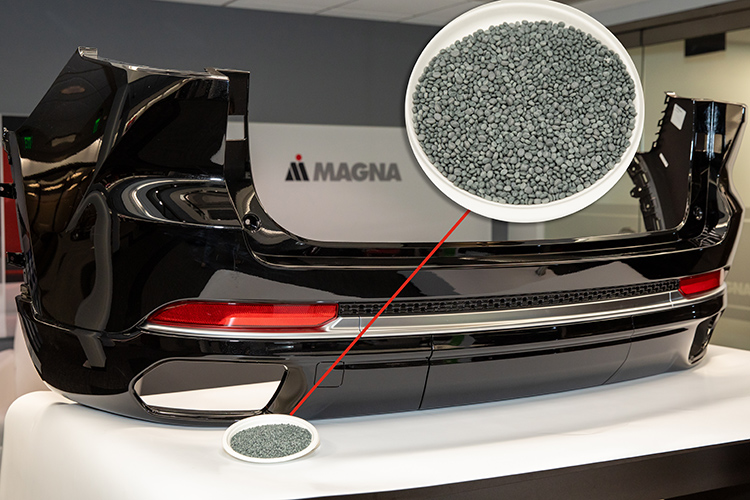
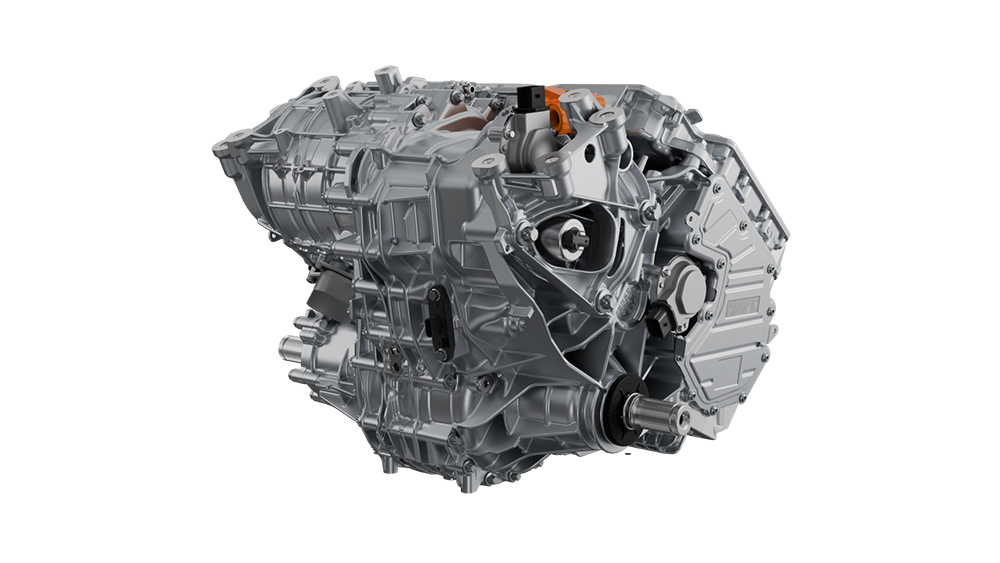
All the examples described here are part of Magna’s innovation pipeline, which includes performance materials, sustainable materials, and materials engineering to support Magna Exteriors. There’s also a strong need to find alternative materials for customers’ service parts.
Regardless of the application, innovative and more sustainable materials, along with waste-reducing processes, can significantly reduce our carbon footprint, minimize waste, and conserve natural resources. This helps mitigate some of the most pressing challenges facing the planet today, such as biodiversity loss, pollution, and the overuse of finite resources like fossil fuels and metals.
Another significant advantage of material advancements is their contribution to a circular economy. Unlike the linear "take, make, dispose" model of traditional manufacturing, the circular strategy aims to keep materials in use for as long as possible through practices like recycling, remanufacturing, and repurposing. This approach is fundamental to Magna’s ambitious net-zero targets, including the company’s goal to reduce Scope 3 emissions by 25% by 2030.
As consumers and businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, manufacturers that incorporate more sustainable materials in their products and more eco-friendly processes in their production will lead the way. Moreover, sustainable materials can foster cost savings over time, particularly as energy-efficient production methods and waste reduction strategies reduce operational costs.
Material science has always been the backbone of innovation for design and manufacturing, and in the new era of mobility, it’s never been more important.